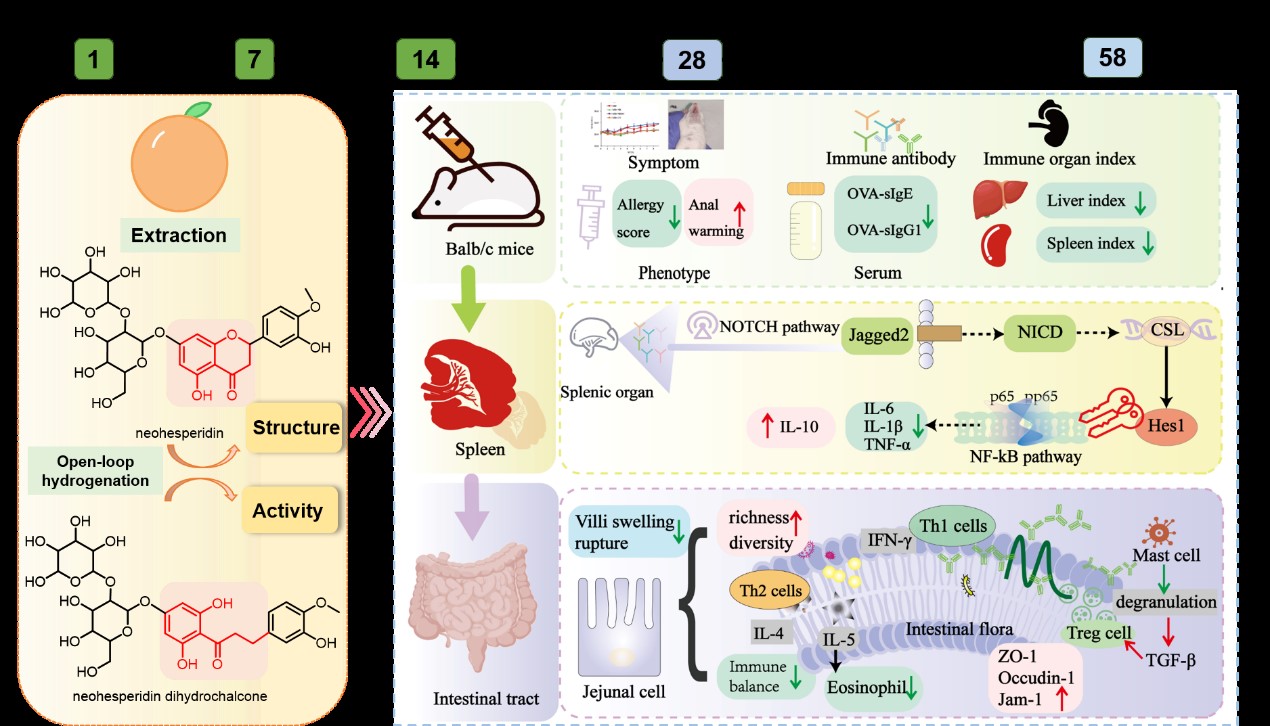
近日,西南大学柑桔研究所加工与品控物流中心团队在食品领域权威期刊《Food Research International》(中科院一区,IF=7.0)上发表标题为“Comparative study on the alleviating effect of neohesperidin dihydrochalcones and its synthetic precursor neohesperidin on ovalbumin-induced food allergy”的研究论文。论文通过比较分析评价研究了柑桔新橙皮苷及其衍生物新橙皮苷二氢查耳酮在缓解食物过敏方面作用活性机制及其构效关系,为开发相关的功能性膳食补充剂产品提供了重要理论依据。

天然黄酮类化合物的生物活性具有结构依赖性。新橙皮苷二氢查耳酮(NHDC)是一种柑桔衍生的二氢查尔酮类天然甜味剂,其甜度高、热量低,是通过对其前体新橙皮苷(NH)(柑桔外果皮中的苦味物质)进行结构修饰而合成的。结构的差异导致化合物味道的差异,也可能导致在功能活性上的差异。我们的结果表明,NHDC在改善过敏症状方面优于NH,特别是在恢复T辅助1和T辅助2细胞平衡以及通过增强与Hes1的结合来抑制脾脏NOTCH/核因子κB(NF-κB)活化方面,通过分子对接得到验证。这些结果为天然黄酮类化合物缓解食物过敏的结构依赖性活性提供了新的见解。西南大学柑桔研究所为该论文第一署名单位,柑桔加工与品控物流中心2022级硕士研究生刘鑫和西南大学食品学院王晨副教授为第一作者,黄林华副教授和白俊英副研究员为共同通讯作者。本研究得到了重庆市科技创新与应用发展计划(CSTB2022TIAD-KPX0079和CSTB2023TID-KPPX0043)、中央高校基本科研业务费专项(SWU-KQ22076)和重庆市研究生科研创新项目(CYS23242和CYS240197)等经费的大力支持。
此外,柑桔加工与品控物流中心团队近期在柑橘功能性物质的营养评价研究方面取得重要进展,研究成果在《International Journal of Biological Macromolecules》(IF=7.7)、《Food Frontiers》(IF=7.5)、《Foods》(IF=4.7)和《Nutrients》(IF=4.8)等食品领域期刊上发表论文,研究结果为柑橘加工副产物的综合利用和产品开发提供了理论依据。
相关论文链接:
1.Liu, X., Wang, B., Tang, S., Yue, Y., Xi, W., Tan, X., Li, G., Bai, J., & Huang, L. (2024). Modification, biological activity, applications, and future trends of citrus fiber as a functional component: A comprehensive review. International journal of biological macromolecules, 269(Pt 1), 131798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131798
2.Tang, S., Wang, B., Liu, X., Xi, W., Yue, Y., Tan, X., Bai, J., & Huang, L. (2024). Structural insights and biological activities of flavonoids: Implications for novel applications. Food Frontiers, 1-30. https://doi.org/ 10.1002/fft2.494
3.Bai, J., Tan, X., Tang, S., Liu, X., Shao, L., Wang, C., & Huang, L. (2024). Citrus p-Synephrine Improves Energy Homeostasis by Regulating Amino Acid Metabolism in HFD-Induced Mice. Nutrients, 16(2), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16020248
4.Tang, S., Ouyang, Z., Tan, X., Liu, X., Bai, J., Wang, H., & Huang, L. (2024). Protective Effect of the Naringin-Chitooligosaccharide Complex on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Systematic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Model in Mice. Foods (Basel, Switzerland), 13(4), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040576
5.Liu, X., Wang, C., Tang, S., Wang, G., Huang, Y., Yang, F., Tan, X., Bai, J., & Huang, L. (2025). Comparative study on the alleviating effect of neohesperidin dihydrochalcones and its synthetic precursor neohesperidin on ovalbumin-induced food allergy. Food research international (Ottawa, Ont.), 212, 116436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116436
 所徽“天圆地方”,反映中柑所人“壹志嘉树”,以推进柑桔科技进步、产业发展为立所根本之严谨风格和博大胸怀;核心的圆形简洁勾画出“柑桔”、形象反映出中柑所专注柑桔科研的行业特征;而围绕主体的弧线代表了科技,象征着中柑所人“修远求索”的治学态度,求真务实的科研精神;星形元素立意中柑所人志在建立一个“方圆”宇宙之间柑桔科研领域的一颗的明星,闪闪发光,惠泽全人类。
所徽“天圆地方”,反映中柑所人“壹志嘉树”,以推进柑桔科技进步、产业发展为立所根本之严谨风格和博大胸怀;核心的圆形简洁勾画出“柑桔”、形象反映出中柑所专注柑桔科研的行业特征;而围绕主体的弧线代表了科技,象征着中柑所人“修远求索”的治学态度,求真务实的科研精神;星形元素立意中柑所人志在建立一个“方圆”宇宙之间柑桔科研领域的一颗的明星,闪闪发光,惠泽全人类。 “壹志嘉树,修远求索”,分别选自中国历史上第一位伟大的爱国诗人屈原《橘颂》和《离骚》中的名句。这八个字是五十年来柑桔所人传承积淀下来的优良传统、精神风貌及办所理念的高度浓缩和凝炼提升,并与中国数千年博大精深的文化底蕴和人文精神相互交融辉映,寓意深远 ...
“壹志嘉树,修远求索”,分别选自中国历史上第一位伟大的爱国诗人屈原《橘颂》和《离骚》中的名句。这八个字是五十年来柑桔所人传承积淀下来的优良传统、精神风貌及办所理念的高度浓缩和凝炼提升,并与中国数千年博大精深的文化底蕴和人文精神相互交融辉映,寓意深远 ...